iMessage vs SMS: Key Differences You Need to Know
In today’s digital age, texting has become an essential mode of communication, allowing us to stay connected with friends, family, and colleagues instantly. With the rise of smartphones, the way we text has evolved, offering a range of options beyond traditional SMS. However, not all text messages are created equal. When it comes to texting on an iPhone, two primary types of messaging take center stage: iMessage and SMS. While both serve the same purpose of sending messages, there are distinct differences in how they operate and the features they offer. From encryption and media sharing to device compatibility, the differences between iMessage and SMS are more than just technical— they shape our overall messaging experience.
In this blog, we will explore the history and evolution of both iMessage and SMS messages and dive deeper into the key features that set them apart, so you can better understand which option best suits your needs in today’s fast-paced digital world.
The History
iMessage History:
- iMessage was introduced by Apple in 2011 with the release of iOS 5. It was designed to offer a more feature-rich, secure, and seamless messaging experience for Apple device users. Unlike traditional SMS, which uses a cellular network, iMessage operates over the internet, allowing users to send media files such as photos, videos, and audio messages. One of its key features is end-to-end encryption, ensuring that messages are secure and can only be read by the sender and receiver. With its integration into the Apple ecosystem, iMessage offers users a cohesive experience across all Apple devices, whether it’s an iPhone, iPad, or Mac. Over time, Apple has continued to refine iMessage, adding features like read receipts, typing indicators, and even app integrations, making it one of the most popular messaging platforms in the world. Additionally, iMessage is exclusive to Apple users, meaning that messages between non-Apple devices cannot take advantage of the platform’s advanced features, limiting its reach to a specific user base.
SMS History:
- Short Message Service (SMS) has been around since the early 1990s and is the standard method for sending text messages across all mobile networks. It works by using the cellular network to send text messages of up to 160 characters. Over time, SMS has remained a simple and universal messaging system, supported by almost every mobile device, regardless of brand or operating system. SMS does not support rich media or encryption, which has led to the development of more advanced messaging platforms like iMessage. Despite its limitations, SMS remains the go-to choice for many due to its universal compatibility across all devices and its ability to function without an internet connection. As mobile technology continues to advance, SMS is gradually being integrated with more modern services like Rich Communication Services (RCS), allowing for some of the features that iMessage offers, such as media sharing and better group messaging. However, SMS still retains its reputation for being reliable, especially in regions with limited internet access or when sending messages on basic phones.
Primary Differences
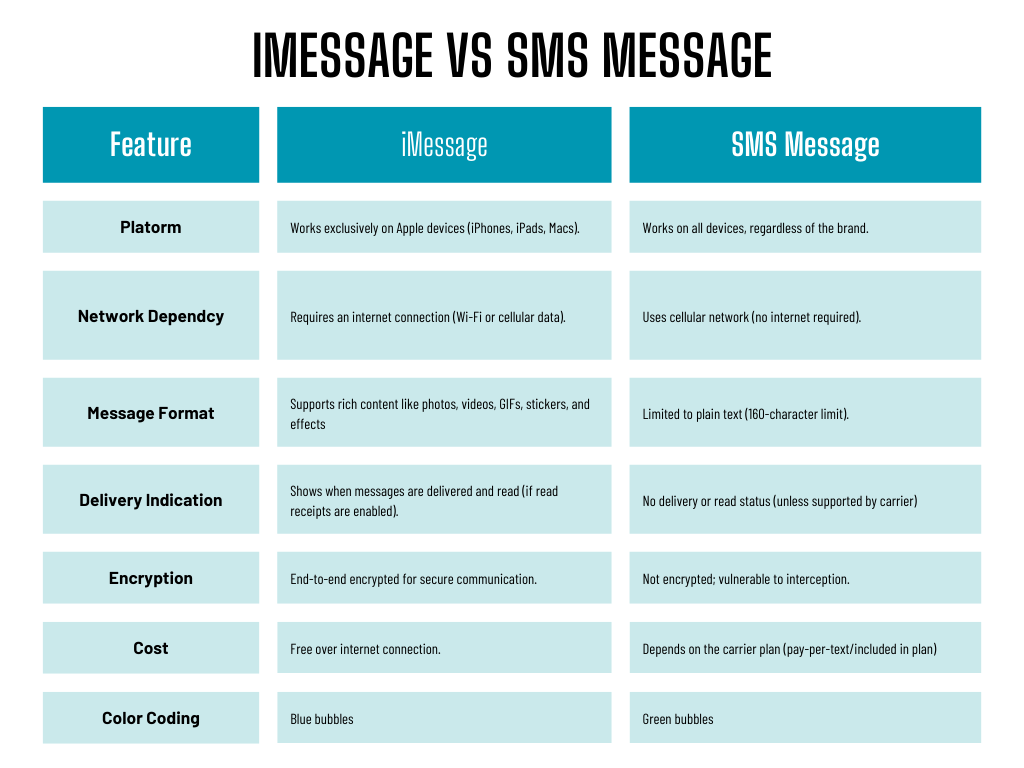
When it comes to digital communication, iMessages and SMS messages are two of the most commonly used messaging systems, but they operate quite differently. iMessages and SMS messages each have unique characteristics that cater to different user needs and technological setups. Below is a detailed comparison highlighting the primary differences between these two messaging platforms:
Consumer Preferences
When it comes to choosing between iMessage and SMS, consumer preferences often depend on factors like convenience, immediacy, and the device they’re using. For many, text messaging stands out as a quick and easy way to communicate, with surveys showing that more than half of consumers prefer it for its simplicity. It’s no surprise that texting has become a dominant form of communication—one study found that over 37% of people prefer texting over phone calls, emails, or even other apps. This trend highlights the strong appeal of text-based communication, with iMessage offering extra perks like media sharing and encryption, while SMS remains a reliable and universally compatible option. However, iMessage’s advanced features like read receipts and real-time typing indicators make it especially popular among Apple users, while SMS continues to be favored by those who rely on basic and universally accessible messaging. Ultimately, the choice between the two often comes down to individual preferences and the devices people use most frequently.
Conclusion
iMessages and SMS messages serve as valuable tools for communication, each catering to different needs and circumstances. iMessages excel in offering a secure and feature-rich experience, enhancing conversations with media sharing, read receipts, and encryption, while SMS messages provide unmatched universality and reliability, functioning seamlessly without the need for internet connectivity. Together, they complement one another, ensuring that communication remains accessible and convenient regardless of the device or situation. Ultimately, both play a crucial role in connecting people, highlighting the importance of versatility and choice in modern messaging.