Understanding Legal Holds [+ How to Implement Them Effectively]
![Understanding Legal Holds [+ How to Implement Them Effectively]](https://www.intradyn.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/Understanding-Legal-Holds.jpg)
Litigation is a common reality for organizations across various sectors today. Whether stemming from competitors, customers, employees, or other unknown factors, the threat of legal action compels organizations to proactively manage their communication records, as these often play a crucial role in legal cases.
As a result, you must be diligent in capturing, storing, and preserving your business communications — in case of a legal hold. Failure to prepare for a legal hold is similar to not buying insurance; if you don’t have it when you need it, it’s too late, and the consequences can be serious.
In this blog post, we will explore the fundamentals of legal holds and provide you with actionable insights on implementing them effectively, ensuring you remain compliant and protected.
What Is a Legal Hold?
A legal hold, or litigation hold, is a process organizations use to preserve relevant information, such as emails and documents, when litigation, audits, or investigations are anticipated, ensuring it is not altered or destroyed. By preserving documentation and electronically stored information (ESI), organizations can mitigate risks associated with the destruction or alteration of evidence that may be critical to legal proceedings.
A legal hold is triggered when a company becomes aware of a pending or imminent legal action or when litigation is foreseeable. Regardless of the cause, the primary purpose of the legal hold is to mandate the preservation of documentation (including ESI) about a grievance or an audit. All processes leading to the disposal of data are suspended to ensure data availability for the discovery process before the actual litigation commences. Amendments to the United States Federal Rules of Civil Procedure (FRCP), have specifically addressed the application of legal holds for ESI, underscoring their significance.
Issuing & Receiving Legal Hold Notices: Key Stakeholders
A legal hold notice is a formal directive that informs custodians (individuals responsible for managing relevant data) of their duty to preserve evidence potentially required for legal proceedings. While these notices are typically issued by the in-house legal team, they can also originate from departments such as IT, HR or compliance.
Issuing a legal hold notice requires collaboration among legal professionals, IT and other relevant departments to define the scope of the hold clearly. This collaborative effort results in a tailored notice that outlines the specific data to be preserved, provides clear instructions for custodians and sets a deadline for compliance. Although email templates can simplify the process, each notice must be customized to address the unique circumstances of each case.
Moreover, as a binding directive, the legal hold notice requires custodians to comply. Failure to do so can lead to significant legal consequences, including sanctions or negative implications during litigation. As such, timely and clear communication is essential. Custodians must fully understand their responsibilities to preserve data as specified in the notice and take appropriate measures to secure that information.
In some instances, legal hold notices are also sent to third parties who may hold relevant data, such as external vendors, service providers or former employees. These parties are equally required to adhere to the legal hold directives and ensure the preservation of pertinent information.
Consequences of Failing to Apply a Legal Hold
Failing to execute a litigation hold properly can have serious legal and financial consequences for an organization. Under the U.S. Amended Rules of 2006, businesses are obligated to preserve relevant information as soon as they become aware of pending or potential litigation or regulatory investigations. If they fail to do so, they risk severe penalties.
Organizations must notify records custodians of their duty to preserve key data and provide clear instructions on how to comply with the legal hold. Delays or failures in applying a legal hold can lead to the loss of crucial evidence, which may jeopardize entire cases and result in adverse legal judgments, sanctions or fines.
In-Place Hold vs. Litigation Hold: What’s the Difference?
An in-place hold and litigation hold are both mechanisms used to preserve relevant data during legal matters, but they serve distinct purposes and operate differently. An in-place hold allows specific items, like email accounts or document libraries, to be preserved in their original locations while still permitting regular access and editing. In contrast, a litigation hold freezes all relevant data to prevent alteration or deletion, enforcing stricter restrictions to ensure evidence preservation for legal proceedings.
An in-place hold can be beneficial in scenarios where business operations must continue without disruption. For example, if an email account is placed on an in-place hold, users can still send and receive emails, but the system ensures that any relevant messages are preserved in their current state. In-place holds are often employed in ongoing investigations or audits where data retention is essential, yet operational flexibility is necessary.
On the other hand, a litigation hold is a more stringent preservation mechanism typically initiated when litigation is anticipated or ongoing. Once a litigation hold is implemented, custodians are required to refrain from accessing or editing the preserved data, ensuring that all potential evidence is maintained in its original state. This type of hold is crucial for safeguarding evidence for legal proceedings, as it minimizes the risk of data spoliation and ensures compliance with legal obligations.
While both in-place holds and litigation holds aim to preserve data, the key difference lies in the level of restriction and access permitted. In-place holds offer flexibility by allowing continued interaction with data, whereas litigation holds impose stricter controls to ensure the integrity of evidence for legal purposes.
When is a Legal Hold Necessary?
The need for a legal hold arises when there is a reasonable expectation that certain information may be relevant to pending or anticipated legal proceedings. This obligation often arises long before any formal litigation begins, making it essential for organizations to act quickly once they foresee possible legal disputes or investigations.
A legal hold may be necessary in a variety of scenarios, such as when an organization:
- Receives a formal notice or communication indicating the possibility of legal action from another party.
- Discovers information or events that point to a potential legal dispute.
- Gets issued a preservation request from opposing counsel.
- Carries out an internal investigation that could escalate into legal proceedings.
- Undergoes significant business changes, such as mergers or reorganizations, that may require securing critical data.
- Faces pending or anticipated litigation.
- Is subject to government investigations.
- Undergoes regulatory audits or internal audits.
- Encounters employee disputes.
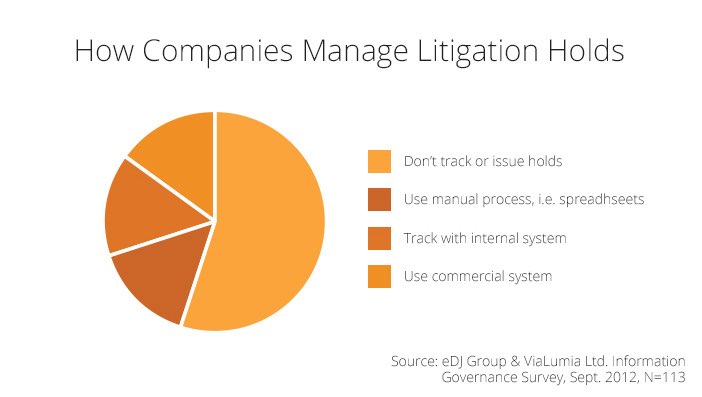
How Companies Manage Legal Holds
Given the various forms of ESI — including computer files, emails, voicemails, videos and images — scattered across multiple locations, such as servers, desktops, laptops, mobiles and data centers, identifying and tracking all relevant document custodians and locations can be a tedious task. Many organizations still depend on manually generated emails and spreadsheets to notify custodians and track their responses, making these methods both time-consuming and risky.
Implementing a Legal Hold: A Step-by-Step Process
The process of implementing and enforcing a legal hold involves multiple steps. Let’s take a look at the step-by-step breakdown below:
1. Identify Trigger Events
A legal hold is triggered when an organization becomes aware of events suggesting a legal dispute may arise. Common trigger events include:
- Filing an administrative claim
- Organizational knowledge of a potential claim
- Conversations with supervisors
- Retainer of counsel and experts
- Compiling a list of opponents
- Receiving a threat-to-sue letter
- Prior events that have led to litigation
External triggers can also include:
- Industry-wide litigation
- Agency investigation
- Service of a lawsuit
2. Assess the Duty to Preserve
After identifying a trigger event, you must assess your obligation to preserve data. This involves determining who within your organization is responsible for deciding if a legal hold is necessary. Conduct a thorough analysis, both organizational and legal, to ensure you fully understand the scope and nature of the hold.
3. Define the Scope of the Hold
Next, you’ll want to define the scope of your legal hold. The scope of the legal hold is determined on a case-by-case basis, taking into consideration various types of ESI and other records. The scope might include emails, system log data and other potential data sources. The key question in this stage is: What is reasonable to preserve?
4. Issue the Legal Hold
Once the scope is defined, it’s time to issue a legal hold notice. The notice outlines the data that must be preserved and is typically sent by legal counsel or relevant departments such as IT, compliance or HR. Ensure that the notice also provides clear instructions to custodians and includes details on the type of data to be preserved and any technical considerations, such as coordinating with IT to reference the data map.
5. Notify & Interview Custodians
Inform custodians of their preservation obligations through a formal hold order. This may involve interviews to determine the scope of discovery and understand which systems and data sources are relevant. Engaging with key witnesses can also provide valuable insights into your data landscape.
6. Temporarily Suspend Regular Data Retention Policies
To prevent the inadvertent loss of relevant information, temporarily suspend your regular data retention and deletion policies. During this period, collaborate closely with your IT department to ensure that all data systems comply with the preservation obligations.
7. Enforce & Monitor Compliance
To ensure compliance, you must monitor custodians and data systems through regular audits and checks. If applicable, consulting with a legal hold oversight committee and collaborating with your IT teams to verify compliance is crucial. Consider issuing periodic reminders and be prepared to adjust the hold’s scope as new developments arise.
8. Modify the Legal Hold
As the case evolves, you may need to adjust the legal hold. This can involve:
- Expanding the hold to additional custodians
- Broadening or narrowing the scope of preserved data
- Adjusting the hold based on new legal requirements or court orders
Be sure to re-check the distribution list and modify the scope of records as necessary to maintain compliance.
9. Document Preservation Efforts
Throughout the process, document all your preservation efforts thoroughly. These records serve as evidence that your organization has taken the appropriate steps to meet its preservation obligations and can be critical in case of disputes.
10. Monitor & Release the Hold
Continue to monitor the legal hold over time. This includes issuing reminders, managing holds for new or terminated employees and conducting audits to verify compliance. Once your legal obligations have ended (e.g., after litigation is resolved), you can formally release the hold, allowing your organization to resume standard data retention practices. Remember to address the cascading hold dilemma by ensuring that all associated holds are lifted.
11. Organize Parties on a Centralized Platform
To enhance your efficiency, consider using a centralized platform to manage the legal hold process. This can streamline communication and coordination among custodians, legal teams and IT departments, ensuring everyone is aligned and can easily access relevant information.
12. Periodically Reassess & Release the Hold
As your legal proceedings progress, regularly reassess the scope of your legal hold. When it is determined that the hold is no longer required, you can formally release it and resume your standard data management practices.
Best Practices for Creating a Systematic Process for Executing Legal Holds
To effectively manage legal holds, you must establish a comprehensive policy that includes essential components and best practices. Let’s take a look at the essential components of a legal hold policy along with best practices for creating a systematic process for executing legal holds:
- Scope: Clearly define and outline the reach of the legal hold policy, including which departments, individuals and types of data are affected. Specify the circumstances that trigger the legal hold, such as litigation, investigations or audits. You can also create and use templates for this.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Outline and identify the custodians involved in the legal hold process and assign clear responsibilities to each role to facilitate accountability and effectiveness.
- Communication Protocols: Provide clear, detailed notifications to custodians. Specify notification methods (e.g., email, meetings) and encourage questions for clarification. Ensure that you communicate regularly with the custodians.
- Process Timeline: Outline the legal hold process phases, including communication timing, duration and termination criteria. Include periodic reviews for compliance and necessary updates, documenting interactions to prepare for court requirements.
- Documentation: Emphasize the importance of maintaining detailed records throughout the legal hold process, such as notifications sent, acknowledgments received and data loss preservation actions. Ensure records are easily accessible for audits.
- Data Preservation Guidelines: Provide clear instructions on preserving relevant data, specifying data types (e.g., emails, documents) and technical preservation methods (e.g., backups, secure storage). Stress the need to avoid altering or deleting relevant data and consider automation for efficiency wherever possible.
- Policy Updates: Establish a procedure for regularly reviewing and updating the legal hold policy. Specify review frequency and responsibility for updates, encouraging stakeholder feedback to maintain relevance and effectiveness. Solutions should be user-friendly, provide real-time updates, be mobile-friendly, secure and sourced from quality providers.
4 Benefits of an Automating Legal Hold Process
As seen in the aforementioned steps, navigating the complexities of legal holds can be daunting for organizations, making it essential to consider the advantages of automating this critical process. Here are the four key benefits of automating your legal hold process:
1. Execution Speed: An automated legal hold process can be implemented as soon as the need is identified. Notifications are sent instantly to document custodians, helping ensure proper and timely preservation of data. Increased efficiency, fewer errors, tracking responses, interviews and data collection from all custodians can be a highly labor-intensive, time-consuming task. Automated tracking can reduce errors from manually handling and tracking responses, data, etc.
2. Repeatability: An automated process can be consistently executed multiple times.
3. Defensibility: Automation improves defensibility by generating accurate documentation of the legal hold process, which can be presented in court if needed. This documentation helps demonstrate compliance with legal requirements, reducing the likelihood of sanctions or penalties.
4. Cost Reduction: Automating legal holds decreases costs by streamlining execution and minimizing the need for manual oversight. Fewer personnel hours are required, and faster, more accurate processes result in significant savings over time.
Why The Legal Hold Process Is Easier With an Archiving Solution
The high volume of communications can make enforcing legal holds challenging, leading to the risk of missing critical emails. An archiving platform is essential for businesses looking to automate the legal hold process, as it streamlines data management and ensures compliance.
An archiving solution centralizes the storage of emails and other electronic communications, minimizing the chances of overlooking vital information during legal holds and thereby protecting organizations from legal repercussions. Automation reduces manual effort while enhancing data retention accuracy, allowing you to tailor legal hold processes to your specific needs. This ensures that all relevant communications are preserved and easily accessible, ultimately safeguarding your businesses’ interests during legal challenges.
Implementing an archiving solution offers additional benefits, such as cost-effective data retention and advanced search capabilities for quick retrieval during legal holds. Furthermore, automated archiving follows documented procedures, providing transparency and accountability.
Take the Next Step in Legal Compliance With Intradyn
Ready to enhance your legal hold process and streamline your data management? Discover how our eDiscovery solution can transform your approach to legal holds and compliance. Download our eBook: Your Go-To Guide to eDiscovery Solutions today to explore best practices, gain valuable insights and empower your organization to navigate legal challenges effectively.